Table Of Contents
In last week’s post, we told you that Ethiopia, Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of the Congo are the most desirable countries 3air looks to launch its services.
We consider Nigeria to be the ‘golden country’ for our launch. It is the largest economy in Africa and within the top 50 economies worldwide, with a GDP of $475B in 2019. This is projected to grow to $736B by 2023 Nigeria is also the largest country in Africa by population and ranks 7th worldwide, with a population of 208.8 million in January 2021. In terms of size, Nigeria is almost 4 times the size of the United Kingdom with half of the population living in cites, and the other half in rural areas.
Our team has conducted extensive research and analysis of Nigeria’s current state of connectivity and its potential for future growth. How many people use the Internet? How big is the impact of reliable Internet in every day life and what difference can we make? Read on to find out.
Internet connectivity in Nigeria
Nigeria has been getting a lot of attention for its great progress in the areas of connectivity and digital transformation. According to the Mobile Connectivity Index, Nigeria was the most improved country in SubSaharan Africa in 2019 and the seventh most improved globally. Progress was driven by a range of improvements across the Infrastructure, Affordability and Content and Services.
There were 104.4 million internet users in Nigeria as of January 2021. The number of internet users in Nigeria is increasing rapidly, growing by 19 million users (+22%) between 2020 and 2021. Internet penetration in Nigeria stood at 50.0% in January 2021.
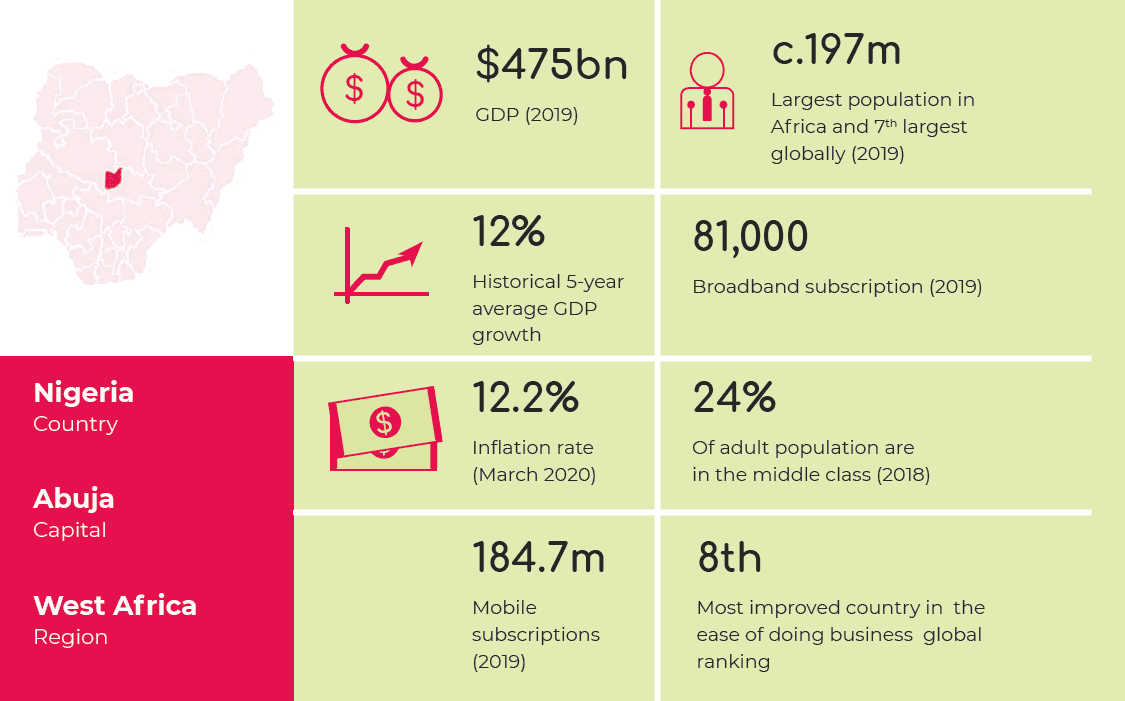
Nigeria country profile
Let’s take a look at the different aspects that are having this positive effect in more detail.
Infrastructure:
3G coverage reached 78% in 2019, with 20 million people covered during the year. After the first 4G networks were rolled out in 2016, operators have reached an average of 45 percent 4G coverage throughout the entire country. Improvements in coverage, especially for 3G, are mainly due to the fact that operators reuse some of their existing 2G spectrum in order to deploy 3G. This allows them to roll out 3G services in an efficient way. Increased 3G and 4G coverage has gone hand in hand with improved network download and upload speeds and lower latencies.
Affordability:
When looking at the affordability of getting online, you need to consider the cost of internet-ready devices, as well as connectivity plans.
Nigeria has some of the cheapest mobile phone prices in the world, since one of its biggest telecom operators, MTN, launched its MTN 3G Smart Feature Phone for $20. The cost of owning a smartphone dropped from 43% to just 12% of monthly GDP per capita.
Mobile tariffs have become more affordable too, with the cost of a 1 GB monthly plan decreasing from 3.3% to 1.5% of monthly GDP per capita between 2016 and 2019. This has helped drive smartphone adoption among adults in the country, which increased from 28% in 2017 to 44% of total connections in 2019.
Content and Services:
The country’s government has made significant improvements to its services provided online. The number of active mobile apps developed per person increased fivefold in a period of only two years. As of 2019, Nigeria was home to almost 2,000 mobile apps developers.
The economic and social impact of better Internet connectivity
Nigeria is often used as a prime example of achieving broader internet coverage and at the same time offering more affordable devices and internet plans that in turn enable operators to roll out more coverage, as usage increases. This has also been shown to have wider economic and social implications.
A recent study by the GSMA and World Bank found that the rollout of mobile broadband networks in Nigeria between 2010 and 2016 increased employment opportunities — especially among women — and reduced extreme poverty by around 7%. This highlights the transformative impact that technology and internet connectivity specifically, can achieve for the poorest individuals in the world.
Broadband internet speeds in Nigeria
While the country has made great improvements in mobile connectivity, the available options for broadband internet are less effective. In fact, Ookla’s global speed index shows that upload and download speeds are better on mobile compared to fixed broadband.
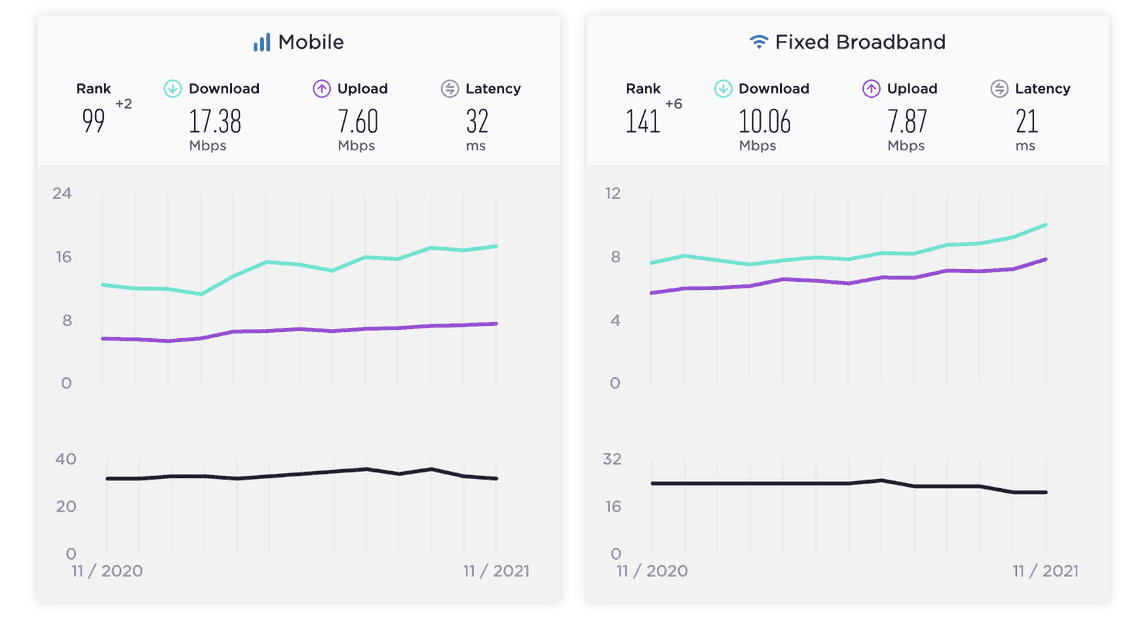
Nigeria Median Speeds, November 2021
Internet availability and cost has improved in comparison to many countries, yet many Nigerian individuals and businesses still complain about a lack of consistent, reliable and stable ISPs.
Young adults looking for employment, freelancers, and SMEs see a difference between the advertised speeds by ISPs on paper, and what is delivered in reality.
The most usual cause of the bad internet connectivity here are the type of cabling (copper or fibre-optic) and their age, the proximity and connection to submarine cables and the size of the country. People report having to work from restaurants or other public areas in order to be close to MTN and Airtel connectivity masts in order to get a decent connection, meaning they cannot work from their home or offices.
3air and K3 Last Mile rollout in Nigeria
3air in cooperation with K3 plans to build the K3 Last Mile solution infrastructure simultaneously in the capital city of Abuja and in Lagos. The two cities have a combined population of over 26M.
K3 already holds an Internet Services License (“ISL”) issued by the Nigerian Communications Commission (“NCC”) under the Nigerian Communications Commission Act. This allows K3 to operate in Nigeria within its ISP scope including broadband, digital TV, and IP telephony services. Following funding, K3 will set up the network, build the infrastructure, train the local team, and launch operations with 4 base stations.
This setup will achieve coverage of about 90% in Abuja and Lagos. The duration of setup from the time of funding till launch will take about 22 weeks.
After launch, each person in the coverage area will have the ability to obtain modern triple play services (internet, Digital TV, IP telephony) equal to that of cable. Upon reaching profitability (with 100 business or 2000 retail clients), we will expand services to other areas in Nigeria.
K3’s Last Mile can deliver up to 1.000 Mbps per end user with download speeds up to 1 Gbps, which represents a large improvement to the currently available internet performance.
In addition all plans have unlimited data capacity. Although the price per MB is going down, the demand for more data is increasingly growing with speed an usability. Havin an uncapped data plan is therefore essential for businesses and households alike.
To read more about K3’s solution and how it works, we highly recommend this article.
If you’re interested in finding out more about the market analysis and timeline for our expansion in Nigeria, check out our doc “Nigeria Operations”.